
LEARNING
STYLES


A learning style is a student's consistent way of
responding to and using stimuli in the context of
learning.
composite of characteristic cognitive, affective,
and physiological factors that serve as relatively
stable indicators of how a learner perceives,
interacts with, and responds to the learning
environment.
educational conditions under which a student is
most likely to learn.
Learning styles are points along a scale that
help us to discover the different forms of mental
representations; however, they are not good
characterizations of what people are or are not
like.
What is a learning
style?

What is learning
process?
It is a characteristic of all human-
being,
It is our need to engage in different
actions
Cognitive style
Describes how the individual acquires
knowledge and processes information.
Cognitive styles are related to mental
behaviours which the individuals apply
habitually when they are solving problems.
Stable and persistent personality dimension
which influences attitudes, values and social
interactions
.

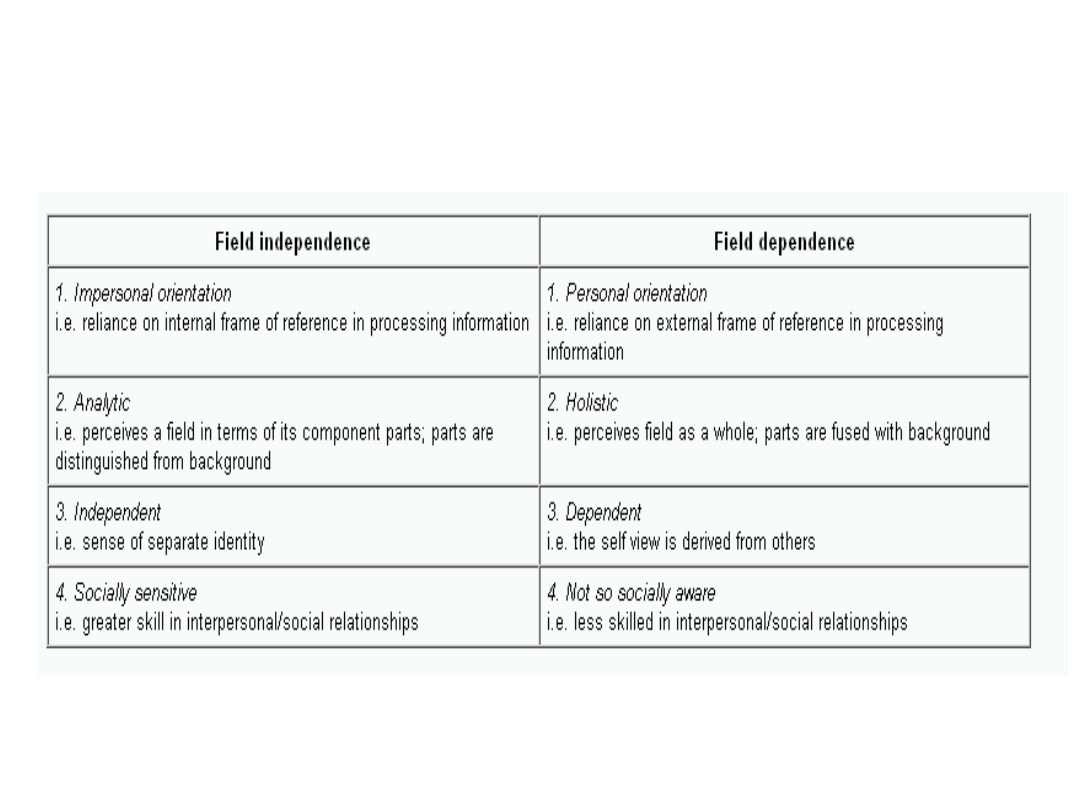
Field independence
A person who can easily recognize
the hidden castle or human face in 3-
D posters and a child who can spot
the monkeys camouflaged within the
trees and leaves of an exotic forest in
colouring books tend toward a field
independent style

the "field" may be perceptual or it
may be abstract, such as a set of
ideas, thoughts, or feelings from
which the task is to perceive specific
subsets.
the tendency to be "dependent" on
the total field so that the parts
embedded within the field are not
easily perceived, though that total
field is perceived most clearly as a
unified whole

Left-and Right-Brain
Functioning
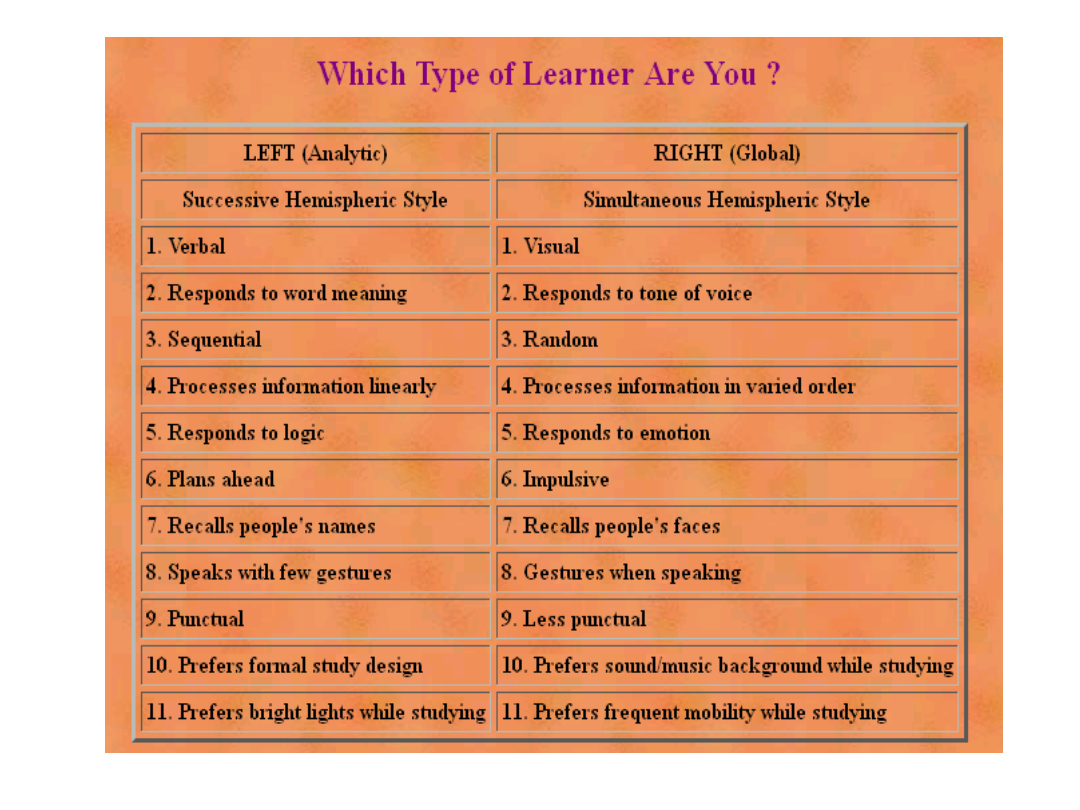
Each hemisphere of the brain functions like two different
personalities with their own way of processing information.
The left brain thinks methodically and likes to organize and
categorize from the environment. It connects new
information with old, making sense of our world.
The left brain connects our internal world to our external
world giving us that feeling of being separate from one
another. It's the left brain that gives us the sense of "I am"
The right brain is that part of our brain that connects us to
each other. In counselling, it's the right brain that gives us
the feeling that our therapist is attuned to us.

Left Brain Function
Language
Logical
Linear
Literal

Right Brain Function
Non-
verbal Recognition
Facial expression
Gestures
Posture
Intensity of response
Holistic
Autobiographical Memory (remembering your
Birthday, significant events)
Map of the body (only on this side)
Stress Management
http://www.myshrink.com/left-right-brain-
function.php


Ambiguity tolerance
is the ability to perceive contradictory
issues which may be difficult to understand
in social and cultural behaviours as well as
information with several meanings in a
neutral and open way.
important issue within the development of
the own personality in education and inter-
cultural communication.

Reflectivity and
impulsivity
It reflects the observation that some
people are more impulsive than
others while processing information
and can reach judgements more
quickly (if not necessarily correctly)
than others who are more reflective
and take their time before reaching
conclusions and acting.

People who are slower than the
median, but score more accurately
than the median, are considered to be
"reflective''. (students who take
extended time on a task and produce
very accurate work)
Those who test faster than the median
but score below the median of
accuracy are "impulsive." (students
who rush through assignments,
frequently missing the correct answers
they also do not consider as many
alternative answers when presented
with open-ended questions as
compared to reflective students)


LEARNING STRATEGIES

What is learning
strategy?
•is thought and action that a learner takes to
understand, store and retrieve knowledge in order to
learn effectively. It relates to input.
•the approach for achieving the learning objects
•is included in the pre-instructional activities,
information presentation, learner activities, testing,
and follow-through
•is usually tied to the needs and interests of
students to enhance learning and are based on
many types of learning styles

I.
Cognitive strategies
Strategies attached to a particular task
which involves the malipulation of the
learning material itself.
A.
Deduction
Consciously applying rules to produce or
understand the second language
B.
Recombination
Constructing a meaningful sentence or
langer language sequence by combining
known elements in a new way
C.
Imaginery
Relating new information to visual concepts
in memory via familiar, easily retrievable
visualisations, phrases, or locations
D.
Auditory representation
Relation of a sound or a similar sound for a
word, phrase, or a longer language
sequence

E.
Keyword
Rembering a word in the second
language by
- identifing a familiar word in the first
language that sound like or
otherwise resembles the new word
- generating easily recalled images of
some relationship between the new
word and the familiar one
F.
Contextualization
placing a word or phrase in a
meaningful language sequence
G.
Elaboration
relating new information to other
concepts in memory
H.
Transfer
using previously acquired linguistic and/or
conceptual knowledge to facilitate a new
leanguage learning task
I. Inferencing
using available information to guess new
meanings of new items, predict
outcomes, or fill in missing information

II.
Socioaffective
strategies
Strategies which require the
involvement of
people and interaction. These
strategies are
connected with feelings and emotions.
A.
Cooperation
working with one or more peers to obtain
feedback, pool information, or model a
language activity
B.
Question for clarification
asking a teacher or other native speaker for
repetition, paraphrasing, explanation,
and/or examples

III.
Communication
strategies
Strategies that are used in
communicative
tasks when you lack knowledge to
convey
the message.

A.
Avoidance strategies
1.
Message abandonment
leaving a
message
unfinished due to language
difficulties
YY: Ummm... why is it called Crater Lake.
XX: Why... called?
YY: Why is it called Crater Lake.
XX: Ah... I'm not sure but... the... maybe
in the first... Um... crater means
the.... Ah... I don't know how to
explain… (laugh)
2.
Topic avoidance
avoiding topic areas or concepts that pose langauge
difficulties
YY: ... Do you ah... do you consider yourself ah...part of the..
what they call the new breed of Japanese young people.
XX: Un.. yes, I think so, but.. I am the... between…new
generation and old people? so called old people.
YY: Um..
XX: Un.
YY: How do you mean between.
XX: Un... cause... (pause) ah... I thi-...
What's what's the the new generation's idea, do you think?

B.
Compensatory
strategies
Compensatory strategies are thinking
strategies that empower the reader
to have a reflective cognitive
learning style that renders
interactive and meaningful dialogue
between the reader and the printed
page
Compensatory strategies
1.
Circumlocution
using many words (such as "a tool used for
cutting things such as paper and hair") to
describe something for which a concise
(and commonly known) expression exists
In other words, it is describing or exemplifing
the target object of action, e.g. a thing you
use to open a bottle with for a corksrew

1. Circumlocution
Circumlocution, Paraphrase, or
Description
YY: What kind of work.
XX: Oh, oh.. I was working now eh... Develop and..fine-line
pattern, (laugh) uh... circuit board, like circuit board.. very
fine.
YY: Uh huh..
XX: Uh.. fine line, and... very very narrow.. line.. On a board.
YY: So, it's a new.. new kind of IC or something like...
XX: No no no no... circuit board, full circuit board...IC is settled
on this.. circuit board.

2. Approximation
using an alternative term which expresses the
meaning of the target lexical item as closely as
possible, e.g. ship for sailboat
3. Use of all-purpose words
Extending a general, empty lexical item to
context where specific words are lacking, e.g.
the overuse of thing, stuff, you can call it
thingie

4. Word coinage
creating a nonexisting L2 word based
on a supposed rule, e.g. you call
vegeteriansit for vegeterian
And... at the mountain, we.. get off the taxi, and..
climb.. the mountain. It takes.... in total we have we
are.. We stayed...two... sleep..... s::leep days in the
mountain.
* (“sleep day” = night)

5. Prefabricated patterns
using memorised stock phrases,
usually for ‘survival’ purposes
6. Nonlinguistic signals
These are mines, gestures, ficial
expression, or even sound imitation

7. Literal translation
translating literally a lexical items, idioms, compoud
words (word is made when two words are joined to
form a new word, e.g. waterfall, keyboard,
playground, etc.), or structure from L1 to L2
YY: Ya, ah...I live in..the my house, that is the ah...bag
shop.
XX: ...
YY: BAG.
XX: Bag shop...

8. Foreignizing
using L1 word by adjusting it to L2
phonology and/or morphology, e.g.
by adding to it a L2 suffix
and when I.. when I did a.. parttime job at ... a
department.
* (“Department” = department store)
9. Code-switching
using a L1 word with L1 pronuncation or a L3
word with L3 pronuncation while speaking in
L2
10. Appeal for help
asking for aid from the interlocutor either
directly (e.g. What do you call it?) or indirectly
(e.g. by rising intonation, pause, eye contact,
puzzled expressions, etc.)

11. Stalling or time-gaining
strategies
using fillers or hesitation devices to fill
pauses and to gain time to think, e.g.
by using expressions such as well, let
me see, now let’s see, uh, as a
matter of fact, etc.

How can the teacher develop
learners’ strategies?
• Ask and find which strategies they
are already using – they can share
their ideas
• Teach strategies directly and help
students incorporate them into tasks
• Encourage students to use them
• Use the techinique THINK ALOUD –
say what you’re doing while
performing the task

THANK YOU FOR
YOUR ATTENTION!!!
HOPE YOU’VE
ENJOYED IT
Document Outline
- LEARNING STYLES
- Slide 2
- What is a learning style?
- What is learning process?
- Cognitive style
- Field independence
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Left-and Right-Brain Functioning
- Left Brain Function
- Right Brain Function Non-verbal Recognition
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Ambiguity tolerance
- Reflectivity and impulsivity
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- What is learning strategy?
- I. Cognitive strategies
- A. Deduction
- C. Imaginery
- E. Keyword
- F. Contextualization
- H. Transfer
- II. Socioaffective strategies
- A. Cooperation
- III. Communication strategies
- A. Avoidance strategies
- 2. Topic avoidance
- B. Compensatory strategies
- Compensatory strategies
- 1. Circumlocution
- 2. Approximation
- 4. Word coinage
- 5. Prefabricated patterns
- 7. Literal translation
- 8. Foreignizing
- 9. Code-switching
- 11. Stalling or time-gaining strategies
- How can the teacher develop learners’ strategies?
- Slide 43
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
2 Learning strategies and styles
Honey and Mumford Learning Styles, Studia, Zarządzanie, zachowania organizacyjne
The Relation Between Learning Styles, The Big Five Personality Traits And Achievement Motivation
Dyslexia and learning styles
learning styles
Ebook Education Ways Of Learning 2E; Learning Theories & Learning Styles In The Classroom Routled
jobs and life styles (2)
CHAPTER 1 HRM, strategy and the global context
Prywes Mathematics Of Magic A Study In Probability, Statistics, Strategy And Game Theory Fixed
85 ?sic Strategies and Group tactics using screens
Strategy And Tactics For Novice Players
Anders Wivel Security Strategy and American World Order, Lost Power (2008)
Kwiek, Marek Concluding Remarks European Strategies and Higher Education (2012)
Searching for the Neuropathology of Schizophrenia Neuroimaging Strategies and Findings
Case study Strategy and Society, Porter&Kramer
Ebsco Garnefski Cognitive emotion regulation strategies and emotional problems in 9 11 year old ch
M Euwe Course of chess lectures, Strategy and tactic (RUS, 1936) 2(1)
Ebsco Garnefski Cognitive coping strategies and symptoms of depression and anxiety a comparison be
więcej podobnych podstron